There are two carotid arteries located each side of the neck which are the major arteries that supply blood to the brain.
Carotid artery disease occurs when there is a narrowing or blockage in one or both carotid arteries which reduces blood supply to the brain. This disease is typically caused by atherosclerosis or a build up of plaque in the internal carotid arteries. Carotid artery disease is the major cause of stroke and mini stroke (Transient Ischaemic Attack or TIA).
Causes of Carotid Artery Disease (CAD)
OR Request an Appointment
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease (CAD)
These symptoms are very serious and require immediate medical assistance.
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Disease (CAD)
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery disease hopefully occurs before the onset of a stroke. In these circumstances it is usually picked up by examination of the carotid arteries with either an ultrasound or CT scan.
Treatment of Carotid Artery Disease (CAD)
Carotid artery disease is treated to prevent a stroke.
Carotid artery stenosis (narrowing) can be treated via two procedures:
Dr Brendan Stanley is one of the few Vascular and Endovascular Surgeons in Perth who perform both carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting and therefore he is able to provide the safest and best procedure for each individual patient.
Endarterectomy
Endarterectomy is a surgical operation where an incision in the neck is performed to gain access to the carotid artery. The artery is then opened up and the plaque build up within the artery is removed. The carotid artery is then closed with a suture.
Carotid Artery Stenting
Carotid artery stenting is a minimally invasive procedure where an expandable nitinol tube is inserted into the carotid artery to open the narrowing and restore blood flow to the brain. This stent procedure is performed under local anaesthetic and sedation via a small incision in an artery in the groin which allows access to the carotid artery in a very similar technique to stenting of the coronary arteries of the heart.
About 70% of Dr Stanleys patients with Carotid Artery Disease can be treated with stenting. This usually requires the patient to spend only 2 days in hospital after the procedure. In the 30% of patients not suitable for stenting, an open carotid endarterectomy repair is required.
Stenting or endarterectomy is recommended for symptomatic carotid stenosis (which means that the patient has had a stroke or TIA) as treatment prevents the incidence of further strokes.
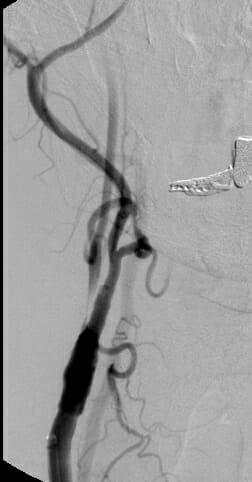
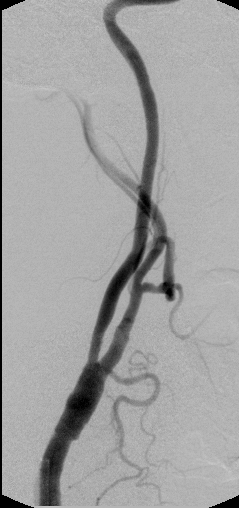
Asymptomatic Carotid Disease
Asymptomatic carotid artery disease occurs in patients who have carotid artery stenosis/narrowing that has not caused a stroke or mini stroke. Treatment is still performed, however the criteria for treatment is more rigid when compared to symptomatic carotid stenosis. This is because the benefits for treating asymptomatic stenosis is not as great as for symptomatic carotid disease.
Each patient with an asymptomatic stenosis is thoroughly investigated so as to have their medical management optimised and treatment options discussed.
